'Hands-on Help for SMEs' and Smart Technical People'
Virtual and Augmented Reality
Revolutionising complex product development and making the
factory of the future a reality for today’s manufacturers
VR & AR: What it all means for Industry
Virtual and Augmented reality technologies are starting to revolutionise complex product development and production processes. It’s an exciting area impacting many high-tech industry sectors at the moment, but increasingly trickling down the supply chain to SMEs too.
Virtual and Augmented Reality – What are they exactly?
In the context of manufacturing and product design Virtual Reality (VR) digitally simulates a product or environment, often with the user being able to interact and immerse themselves within it. With Augmented Reality (AR) the digital product or information is projected on to a real world background, rather than a digitally simulated one like VR.
Virtual and Augmented Reality for Design Development
From a product development perspective VR and AR help to refine and optimise designs at an early stage. Concepts and options can be reviewed, adjusted and modified quickly. Digital models can also be virtually tested, analysed and simulated with tools like FEA and CFD. The result is rapid iterative design cycles and ultimately great products. Importantly you can get cross-functional team input, including potential clients.
VR and AR make animated simulations possible so you can see how products will be used over time. This is invaluable if you are serious about understanding how products will be used, with factors like ergonomics, access, look and feel coming into play. Anybody can understand a life-like simulation, whereas 2D engineering drawings and more complex 3D models can be difficult to interpret if you do not possess a technical background.
Ultimately VR and AR aid communication and buy-in during product development. The result is reduced technical risk, with a greater probability components and products will be fit for purpose.
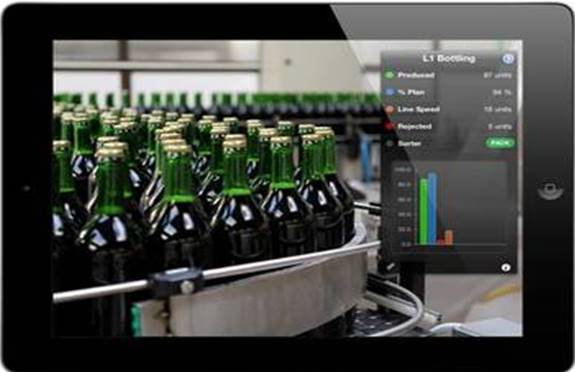
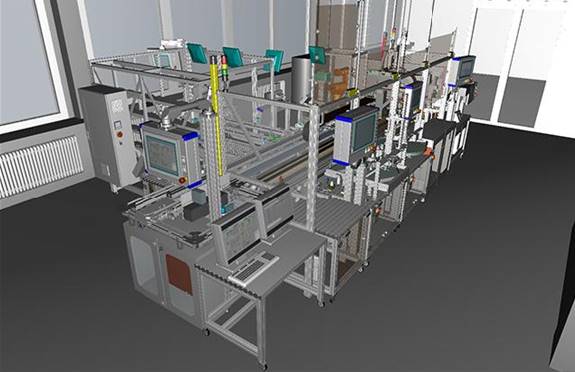
Virtual and Augmented Reality for Production
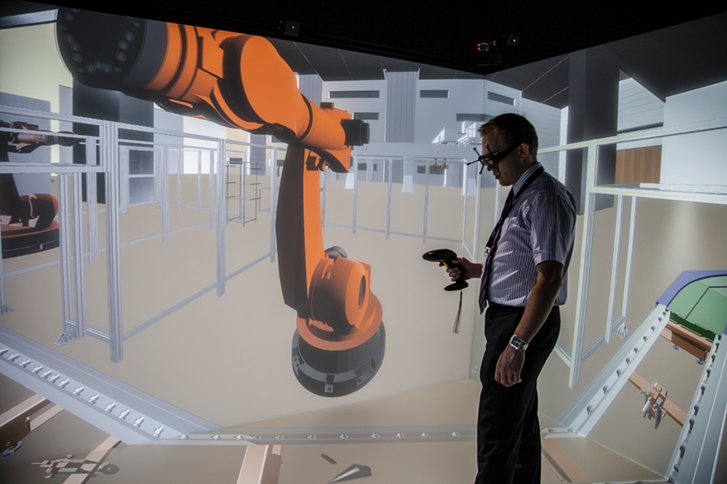
Manufacturing and production have huge amounts to gain from VR and AR. Businesses are now planning their production and assembly processes out in full in a virtual world. In turn this is used to speed up factory and plant commissioning and operation. In practical terms manufacturers have used virtual and augmented reality to…
- Structure and optimise the location and flow of production lines.
- Position automation lines, robots, production cells and importantly people, to maximise productivity and efficiency, as well as reduce inventory.
- Operate and handle virtual tools and equipment. Rehearse and train staff for the real thing.
- Factor in the ideal ergonomics for fitters, technicians and other operatives in terms of reach, leaning, twisting and bending.
- Plan around support pillars, lighting, heating and air-con ducting.
- Factor in access for maintenance, cleaning and line-side delivery.
- Scan in an existing factory environment and lay it out with new virtual production lines and equipment.
Do all of the above before placing big orders to the detriment of your cash flow. If you have production facilities the potential is simply huge.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Industry
More and more manufacturing and engineering businesses are realising what AR and VR can do for them. Industry sectors taking advantage include aerospace, automotive, energy, defence and medical. Prime manufacturers are increasingly integrating their supply chain SMEs into their AR and VR set-ups, with digital models and cross-functional teams directly plugged in. Also for SMEs, regional providers are increasingly keen to help smaller businesses access and use AR and VR facilities; an example being the Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre here
For case studies and applied examples see the links below. The range of uses engineers are finding for AR and VR appear to be growing month-on-month. It’s a versatile technology that offers massive potential to savvy SMEs eager to embrace the future. With the broad range of benefits there for the taking why not take a look below and find out more?
Enjoy!
Mark Lynch
Advice Manufacturing
Virtual Reality Motor Maintenance - by Mechatraining LLC. Realistic virtual reality training
demonstrating the assembly maintenance featuring disassembly tools, instructions and sequence.
Augmented Reality in Manufacturing Documents - by uglykid.org. Manufacturing documents contain markers for AR models of the featured components that can be viewed through iOS devices. Downloadable apps make this a real possibility for design reviews in your business or to differentiate your consultancy for your clients.
Collaborative Immersive 3D Room (Courtesy of Immersion3D). Immersion created a collaborative and immersive 3D room (also known as a Virtual Reality room) for Alstom Transport. Discover this VR equipment, its uses and benefits.
Virtual Reality Training Demonstration - by SimLab Soft. Using virtual reality to provide immersive tech factory training for operatives, highlighting problems, hazards and solutions. Demo also includes realistic audio, directions and specific instructions.
VR for Engineering from Vatalis
Virtual Reality is now a valuable tool throughout the product life-cycle. Operations teams can review virtual prototypes to highlight engineering issues earlier, to better understand the human factors implications and to be able to train production line staff to get it right first time. This improves product build quality and reduces errors and levels of rework. It also reduces end-user issues and warranty claims.
Virtalis provides immersive VR technology for engineering environments as a communication hub, where barriers are broken down and everyone is able to interact and speak the same language; whether they are management, engineers, production line workers, designers, marketers or accountants.
Manufacturing Lines Development - Virtual Assembly / Disassembly Validation (courtesy of ESI Group). Perform Virtual Validation of Manual Assembly/Disassembly within a 3D immersive environment:
- Allows early communication and coordination between the groups participating in digital engineering and production verification processes.
- Virtual validation in early phases of production development; verifying suitable tools and assembly processes, initiating considerable savings in production and manufacturing development.
- IC.IDO allows virtual Try-Out of an assembly process based on a digital model in an early production development phase, ensuring a reduction in development cycle.
- Costs reduction, enhancement of the validation depth and quality, continuous optimization of product development times with enhanced product diversity.
- Virtual validation of manual assembly helps to create the production processes planning certainty without using hardware prototypes
Engineering Cars in Virtual Reality (provided by the Engineer UK). The Engineer paid a visit to Warwick University and Jaguar Land Rover to find out how virtual reality is changing the automotive design process.
Range Rover Evoque Virtual reality Cave (by Land Rover Nieuws). Demonstrating how virtual reality is a key tool for Jaguar Land Rover's engineers during the development process. See how it is used to optimise and refine designs and plan for manufacturing.
Immersive Operator Training (Courtesy of Siemens). Siemens COMOS Walkinside enables the usage of 3D engineering data from the basic and detail engineering phases throughout the entire asset lifecycle. Highly complex process plant models can be represented realistically in three dimensions, with COMOS acting as a global data center.
Up-to-date plant data is always available and can be used not only for engineering and monitoring purposes, but also for operation and training. Service and maintenance work can be planned, simulated and executed efficiently.
COMOS Walkinside offers powerful solutions for 3D virtual reality model building and viewing. It can be used for immersive operator training and delivers tools for efficient data exchange with third party applications as well as distributed real-time collaboration.
New digital design processes and tools are revolutionising the manufacturing industry (Courtesy of the Engineer). Manufacturing is changing. The advent of new ways to design things and build them is having an effect not only on the products that factories make but also on the factories themselves, and engineers are increasingly using tools such as virtual reality (VR) to put themselves... more
Augmented reality enhances plant floor view, productivity (Courtesy of controleng.com). Automation Integrator Guide: Technology integration provides augmented reality view of industrial plant floor to streamline equipment maintenance, reduce downtime, and improve bottom line more
Virtual reality factory demonstrator launched at the MTC (Courtesy of the IET)
A 3D virtual reality demonstrator designed to make designing new manufacturing processes easier has been launched at the Manufacturing Technology Centre (MTC) in Coventry. The immersive, 3D virtual reality environment allows users to interact with a ‘living lab’ which has been modelled from an existing real-world machine.
The machine mimics a continuous production environment and allows universities, manufacturers and other stakeholders to innovate production processes using the latest technologies that help improve productivity, quality and energy efficiency. more
Using Virtual Reality to analyse and improve design and manufacturing processes by Professor James Richie, courtesy of the Institution of Mechanical Engineering. The digital engineering group at Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh carries out research into digital tools, including virtual reality (VR), and evaluates how these can support engineers. More...
A definitive guide to virtual reality, including a comprehensive section on augmented reality. The site also features useful information on VR in engineering and industry. For a detailed, thorough explanation of this great technology Virtual Reality is definitely worth a good look. More.
Visualisation and Virtual Reality Forum - facilities, expertise and assistance available for manufacturing and engineering Businesses (UK Only)
Visualisation and Virtual Reality (VVR) enables UK manufacturers to visualise their plant, products and processes in ways that were previously out of reach or imagination. The AMRC, MTC, NAMRC and WMG form the core of the High Value Manufacturing Catapult Visualisation and VR Forum.
The Forum promotes the use of advanced immersive visualisation to aid manufacturing companies. Recent applications have included factory layout planning, collaborative design reviews, virtual prototyping, assembly training and human factors assessment. These in turn can lead to;
- Cost Reduction
- Risk Reduction
- Time Reduction
- Quality Improvements
- Improved Knowledge Transfer
The forum also has the capability to hold collaborative design review and training sessions with geographically distributed centres joining together in one shared virtual environment. More
|
Immerse UK brings together industry, researchers and research organisations, the public sector, innovators entrepreneurs, and end users to support the UK in becoming the global leader in applications of immersive technologies: high-end visualisation, virtual, mixed, and augmented reality, haptics and other sensory interfaces with data. By signing up you become part of our Immerse UK members directory and community and are featured on our UK website so others can find out more about what you do. We are committed to supporting our members by: 1) helping to connect people to explore future collaborations, 2) pointing to the latest funding and finance opportunities from across all industries, 3) addressing the issues that slow down R&D and barriers to innovation, 4) identifying the opportunities for growth in the emerging marketplace. |